- Geomembranes are widely used for containment of liquids, solids and waste materials by virtue of its characteristics; resistance to a wide range of chemicals, reliable in exposed environments due to high UV protection against degrading and low temperature brittleness. CeTeau offers a wide range of materials capable of meeting the ever increasing environmental demands.
- Application
• Landfill Liners and caps Reservoirs, irrigation canals, industrial ponds and lagoons
• Recreational lakes, ponds and golf courses
• Agriculture, shrimp farming
• Mine tailings & heap leach pads
• Secondary containment of storage tanks
• Floating covers - Installation
Geomembranes are heat welded in the field by certified technicians using the following welding systems;
Hot wedge weld: a heated (metal) wedge is drawn between the liner, so that the material melts. By using pressure rolls the layers are converted to a homogeneous joint.
Hot air weld: instead of using a wedge, the liner is heated with hot air and pressed together.
Extrusion joints: a bead of melted HDPE is laid on the edge of the liner by using a hand extruder. This forms an excellent joint with the liner underneath.
The large width (7.5 m) of CeTeau geomembranes reduces the number of welds considerably. To guarantee the quality of the welds, all welds are tested in the field.




















- High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Geomembrance
Polyethylene is a long-chain hydrocarbon thermoplastic material obtained through the polymerization of ethylene. Polyethylene geomembranes were developed exclusively to reduce the hydraulic conductivity of earthworks and are part of one of the most sophisticated and effective impervious systems known to date. They are also very reliable in exposed environments due to their excellent resistance to brittleness in low temperatures and superior protection against UV degradation. Manufactured in wide rolls, polyethylene liners come in varying thicknesses ranging from 0.5 to 3.0 mm to meet engineering design requirements.
Surface finish Polyethylene liners come in a variety of surface finishes, from smooth to heavily textured. Offering higher friction properties, textured materials are perfect for lining steep slopes to prevent the slippage of adjacent materials. The level of texturing is described by the asperity heights, which can reach up to 0.25 mm.
HDPE (high-density polyethylene) is the most chemically resistant member of the polyethylene family on account of its dense configuration (>0.94 g/cm3). It is extensively used for containment structures. Although less flexible than its LLDPE counterpart, it still offers great elongation properties allowing up to 12% deformation at its yield point.
LLDPE (linear low-density polyethylene) as its name implies, is a lower-density polyethylene is a lower-density polymer (<0.939 g/cm3) yielding increased material flexibility. LLDPE is mainly used where long-term large settlements are anticipated such as landfill covers.
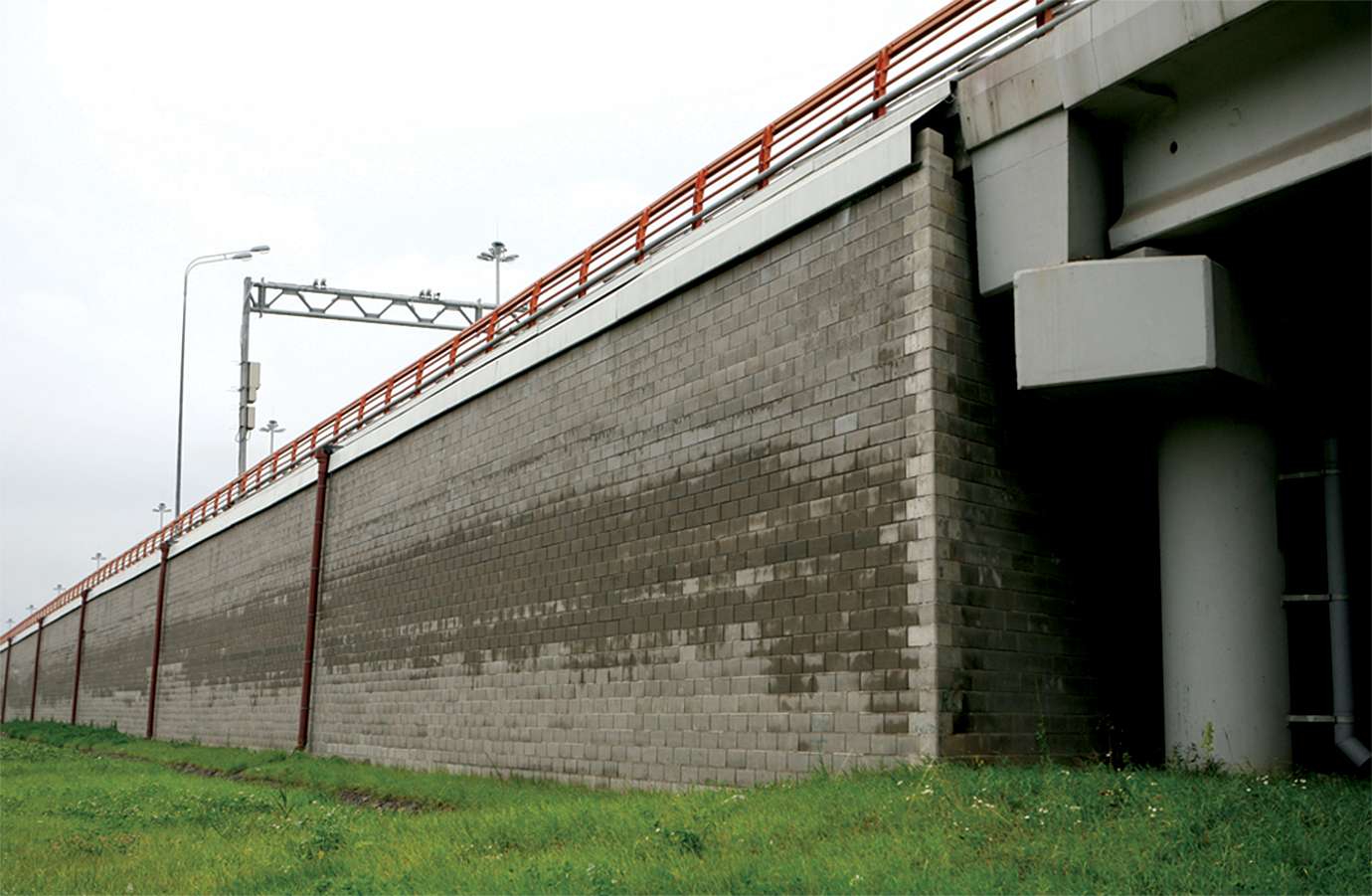

CeTeau Block Wall
CeTeau segmental reinforced blocks wall, Economical, Flexible...
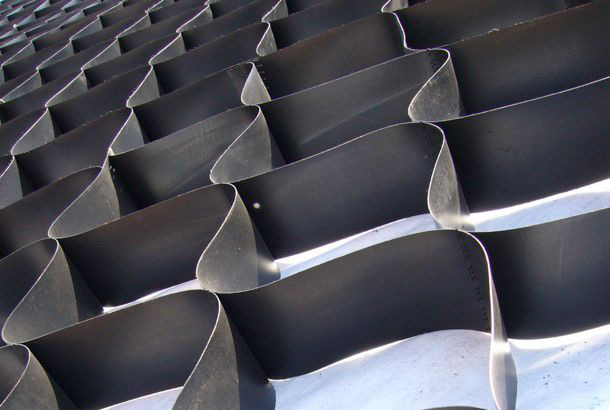

CeTeau Cell
CeTeau cell provides excellent protection for slopes against...
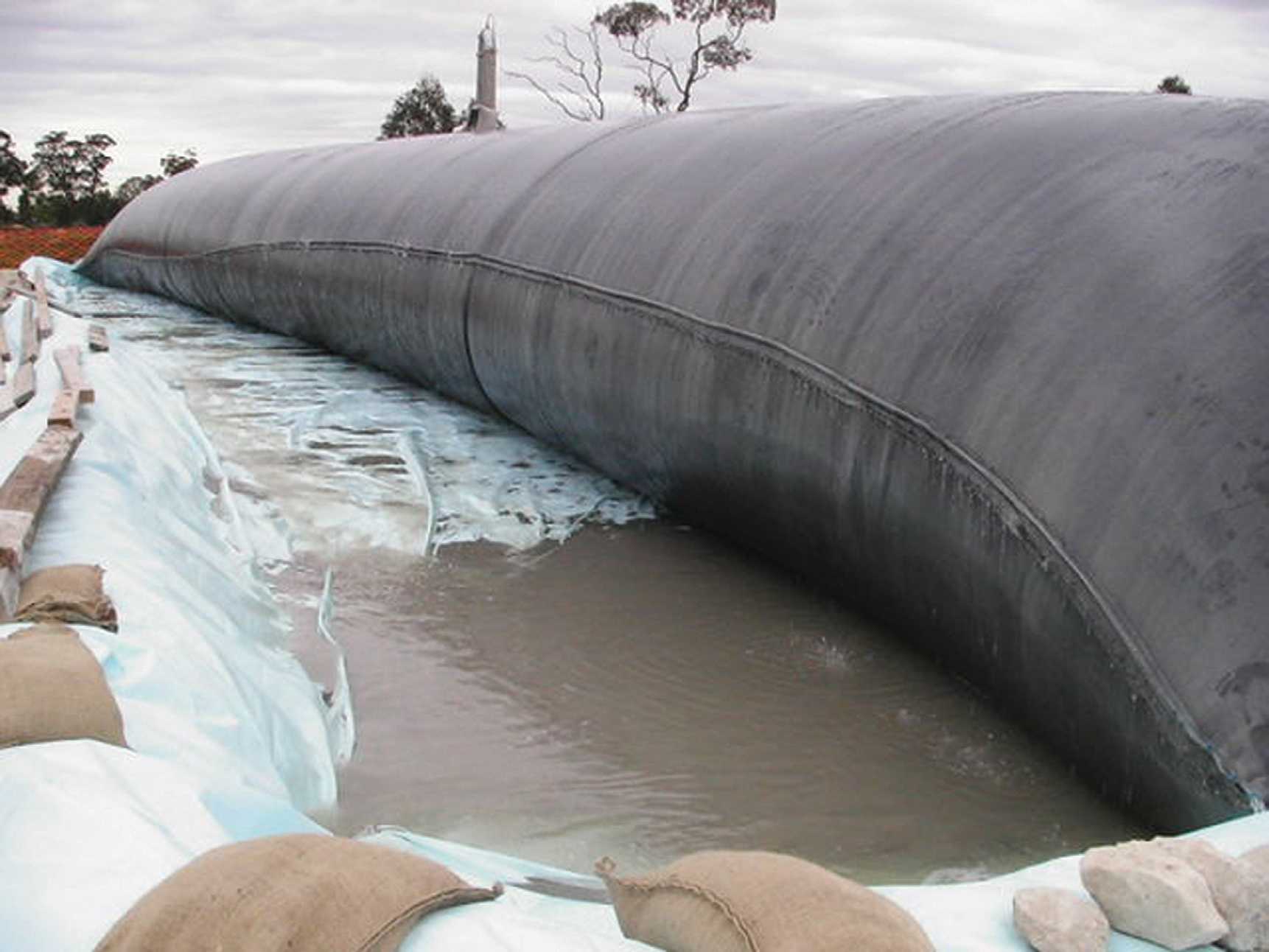

CeTeau Tube
The use of geotextile manufactured into a containment product has ...

CeTeau Geogrid
Geogrids have been developed to overcome the bearing limits of ...

CeTeau Clay Liner
Geosynthetic clay liners are high - performance environmental liners ...

CeTeau Tex
Geotextiles have secured a valued and permanent place among ...

CeTeau Liners
Geomembranes are widely used for containment of liquids, solids ...

PVC Sheet Piles
CeTeau PVC sheet piling systems are the new standard with many ...

CeTeau Gabions
For over a century, triple twist hexagonal mesh has been used ...

CeTeau Silt Protector
Silt Protector is a flexible membrane product that has ...

CeTeau Stripdrain
The use of CeTeau composite strip drains for lateral drainage ...

CeTeau Pumps
We have developed a special vacuum pump for the vacuum ...

Timber Wall Retention
CeTeau timber wall retention is a structurally engineered walling ...
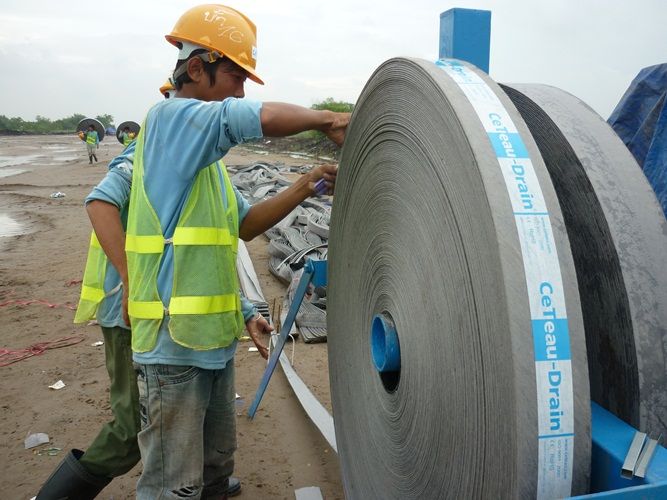

Vacuum Consolidation
The innovative CeTeau Vacuo is designed to accelerate the ...
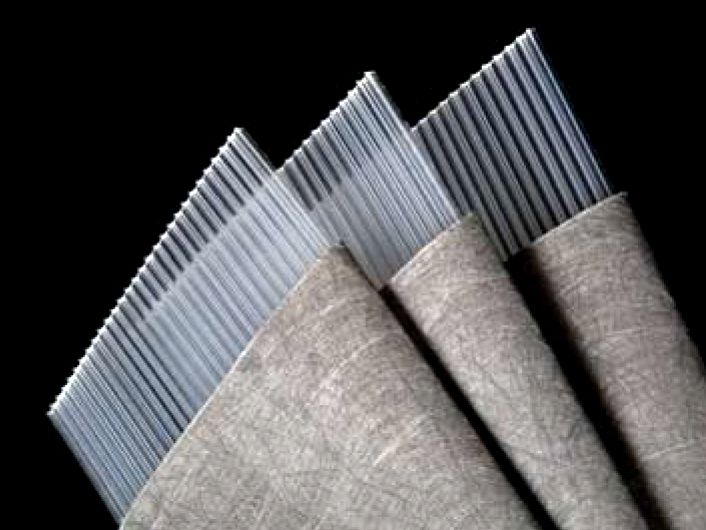

Vertical Wick Drain
Prefabricated Vertical Drains (PVD), also called Wick Drains, are ...
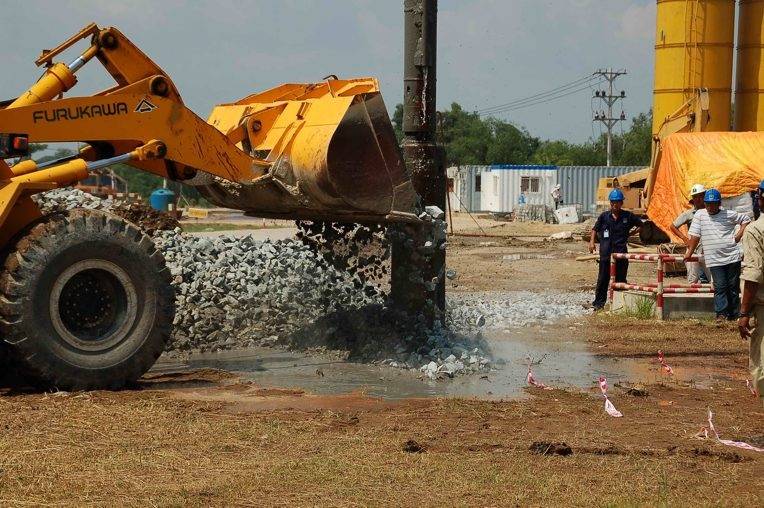

Vibro Stone Columns
In order to be able to offer the full spectrum of soil improvement ...
- CeTeau Timber Wall Retention
- CeTeau Vacuum Consolidation
- CeTeau Vertical Wick Drain
- CeTeau Vibro Stone Columns
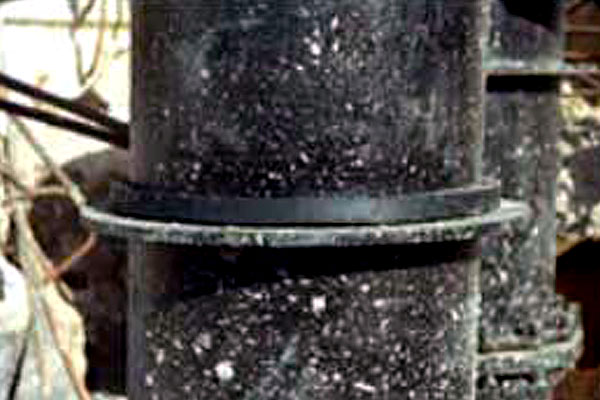

CeTeau Water Stop
Waterstop-RX is a flexible strip-concrete construction-joint ...
- CeTeau Water Stop